As the 2018 Fall Semester concludes, I want to reflect on the first six months of writing this blog. It has been a great honor to share discoveries, explore new ideas, and write about topics related to Technology, Education, and Design. I hope that these TED tips continue to inform and inspire as we celebrate teaching and learning at the University of Wisconsin Whitewater.
Over the last six months, we have explored the difference is between a Learning Management System (LMS) and a Digital Learning Environment (DLE). This distinction is important as it helps to lay the foundation for some of the key decisions applicable to the migration from D2L to Canvas at Whitewater and throughout the UW System.
Canvas has been a source for several posts. The LTC Canvas peer mentors shared some of most important lessons learned while working with Canvas in the classroom. We looked at ways to support communications in Canvas and the importance of making a good first impressions. We explored grading and using Speed Grader in Canvas.
What are some different ways technology can be used in the classroom to support your teaching learning? Tools like Poll Everywhere can increase student engagement and interaction. “23 Things for Digital Knowledge” provided activities that can build student fluency in digital literacy.
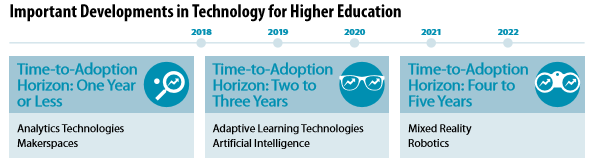
TED Tips have explored the 2018 NMC Horizon Report and its view the trends, challenges, and developments in educational technology as it impacts higher education. Using the Horizon Report provides a lens to highlight pilots and innovative work taking place on campus like Adaptive Learning.
The blog will continue to promote workshops sponsored by the Learning Technology Center and its many partners and collaborators. For example, there is a series of upcoming Canvas workshops this winter: Canvas Open labs, hands on workshops for newcomers to Canvas, Construction Zones to help instructors move their courses from D2L to Canvas, and deep dives into single topics to help with your teaching. Grading in Canvas and building and using rubrics will be explored in early January. For a full list of times and locations of the upcoming winter Workshops visit the LTC. https://blogs.uww.edu/instructional/2018/12/12/canvas-workshops-winter-2019/
The next session in the 2018-19 UW-Whitewater LEARN Center/Learning Technology Center Workshop Series: “Back to Basics to Balance Workload” is Thursday, January 10th from 10:00am to 2:00pm in the University Center. This four hour workshop includes lunch and is designed as a hands-on activity to help prepare for your spring classes! Session Four: Setting the tone early saves time in the long run: Crafting your syllabus and engaging students before the first day of class and beyond.
During the morning session of the workshop, presenters will share evidence-based strategies for creating a more learner-centered syllabus and share tips for engaging students from the first day (and even before class begins!). After a lunch discussion, participants will learn more on how to better utilize Canvas in their courses in a way that clarifies organization and sets expectations in a more transparent manner. Participants will end the session with time to revise their syllabi, first day activities, and/or Canvas course pages and share their materials for small group feedback.
Participants will leave with:
- An overview of best practices for syllabus development
- Experience with a variety of first day activities that can increase student engagement and sense of community
- Ideas to organize their Canvas course pages
- Revised syllabi/activities to enhance student engagement
To register for this workshop: https://my.uww.edu/signup/Registration/Details/15867
Thank you for taking the time to read these posts! TED Tips will return in 2019. Topics next year will build on and support some of the upcoming workshops with TED Tips planned to explore several types of rubrics, building them in Canvas, design of a course homepage, navigation, analytics, and many others. I hope to experiment a bit more in format and content and hope to record the occasional complementary podcast! Until then, have a great holiday break, recharge, and relax! See you next year!
– Ted Witt
Teaching, Learning, and Technology Consultant
Resources
LTC Canvas Peer Mentors http://www.uww.edu/icit/ltc/canvas-portal/peer-mentors
Canvas Workshops Winter 2019
https://blogs.uww.edu/instructional/2018/12/12/canvas-workshops-winter-2019/
LEARN Center/Learning Technology Center Workshop Series: “Back to Basics to Balance Workload.” Session Four: Setting the tone early saves time in the long run: Crafting your syllabus and engaging students before the first day of class and beyond. https://my.uww.edu/signup/Registration/Details/15867