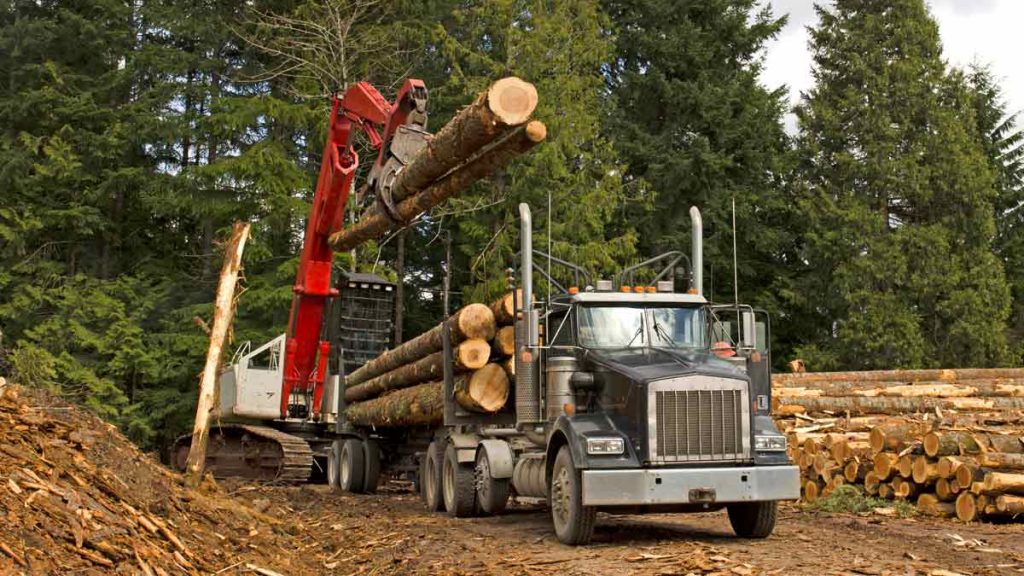
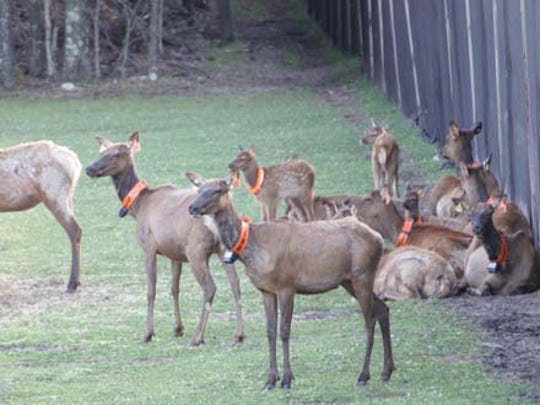
As an avid deer hunter in Wisconsin, chronic wasting disease or CWD is something that always crosses the back of your mind when you field harvest your deer and when you eventually put a fork to it. If you do not know what CWD is, it is a prion disease that affects deer, elk, reindeer, sika deer, and moose. This prion disease is neurodegenerative, meaning that it can result in drastic weight loss (hence wasting), stumbling, fatigue, and other neurological problems. If you have ever seen videos of deer with CWD it is as if you are looking at a zombie but in animal form. It is quite depressing because they no longer have control over their bodily functions. In 2019, the Wisconsin DNR tested around 250,000 deer across Wisconsin. They found that about 6500 of those deer were infected with CWD. Therefore, you could calculate that approximately 2% of the whitetail deer population in Wisconsin is infected with CWD.

Most of these cases are found in the Southwestern part of the state and 2% doesn’t sound like much but it is a problem no matter how small it might be. This is a problem because we know that this disease can be spread to a variety of ungulates, but we do not know whether it can be spread from ungulate to human. Right now, the only thing we do know is that CWD poses a risk to non-human primates like monkeys that eat meat infected by CWD. This is somewhat concerning since we are very closely related to monkeys. Though no human has contracted CWD from consuming meat from an infected ungulate it is still a very big concern among hunters. If a human ever contracted CWD we could only assume that it could be transferred from human to human and ultimately becoming the next pandemic.