This week, I conclude the three part series exploring the New Media Consortium’s Horizon Report. The report “identifies and describes the higher education trends, challenges, and developments in educational technology likely to have an impact on learning, teaching, and creative inquiry.” This week focuses on developments in educational technology.
These developments were chosen because they are likely to drive technology planning and decision making and are organized in time intervals related to their approximate time of wide spread adoption. The report identifies seven broad categories of technologies, tools, and strategies. The categories help us understand where we are today. The developments look ahead where we may be going in the future.
Categories of Technology
Consumer technology are tools originally created for recreational or consumer use. As the technologies become more utilized, they have been used as learning aids. Examples include: drones and wearable technologies like fitness trackers. The move from physical textbook to shorter videos highlights this “consumer demand” driving change in the classroom.
Digital strategies enrich teaching and learning by repurposing older activities for the modern digital classroom. They often reinvent conventional ideas to create meaningful 21st century experiences. The transformation of a pager to a cell phone to a smartphone exemplifies this march towards digitalization. Other examples include: The use of location intelligence (GPS), digital makerspaces, and applying concepts of gamification to the classroom.
Enabling technologies transform what we expect of our devices. The classic example is the voice activated computer as depicted in Star Trek; but more commonly realized through Alexa, Siri, and the Google Assistant. Those enabling technologies allow us to do more things. The trend towards cord-cutting is another example.
Internet technologies represent the underlying digital infrastructure. Internet technologies allow us to interact seamlessly and connect more devices in more ways. The “Internet of Things” is an example of how more components in the wired world are being connected to the internet. Another way to think about this is the idea that the Internet is a “utility” — along with the corresponding Digital Divide that highlight inequalities in the infrastructure.
Learning technologies are resources specifically developed for education. They help make learning accessible and available to all. Our digital learning environment is an example. Learning environments are increasingly customizable and personalized. Online courses and the related mobile learning platforms expand the access of education. Adaptive learning is another example of a learning technology. Larger systems like Lynda.com have been developed that offer training and learning at our fingertips. Fully online programs have redefined higher education possibilities…and created new opportunities.
The rise of social media technologies have changed communication and interpersonal relationships. Students communicate and collaborate quickly online. While research used to be the domain of the library, Google has become our primary search engine. Social networks, crowdsourcing, and issues regarding online identity and privacy fall in this category. Students can use sites like Facebook and Instagram to share and retrieve information and multimedia quickly.
Important Developments in Technology for Higher Education
Finally, visualization technologies are a growing set of tools that allow for large sets of information to be analyzed and displayed. They enable easier data driven decisions by making the complex simple. Large sets of information can be visualized in real time. New areas of virtualization and augmented or mixed realities fit into this broad category. Another example is 3D printing.
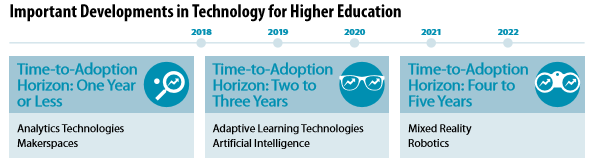
With the categories in mind, I want to briefly identify the important developments in educational technology for higher education as identifies in the Horizon Report. A key criterion for inclusion in the report was its potential relevance to teaching, learning, and creative inquiry in higher education.
Time-to-Adoption Horizon: One Year or Less
Analytics Technologies: Data and big data are being used more frequently to support higher education…and there is a continued focus on measuring learning. Using “grades” as an analytics tool for students to measure their success is nothing new. Instructors, students, administrators and teachers are relying on more high tech analytics to provide insights to complete their tasks. For examples, analytics technologies can help identify at-risk students and trigger interventions. Analytics can be used by students to guide and improve their own learning and by teachers to improve outcomes and tailor content in the classroom. Post education career options can be enhanced by connecting into resources liked LinkedIn that offer data-driven, analytics to help customize pathways to employment.
Makerspaces work by bringing together experts and novices from a variety of disciplines to design, build, invent, and rethink various products. Makerspaces connect higher education and industry. These spaces often include computers, power tools, 3D printers, and other technologies. A perceived benefit of makerspaces is that it engages learners to develop hands-on learning.
Time-to-Adoption Horizon: Two to Three Years
Adaptive Learning: Last week we explored a pilot project on Adaptive Learning here at the University of Wisconsin Whitewater. Adaptive learning is one technique for providing personalized learning, which aims to provide efficient, effective, and customized learning paths to engage each student. Finding the correct applications, developing the pathways, implementing the solutions, will take time.
Artificial Intelligence is no longer in the realm of fiction! Amazon uses it to predict products you may be interested in (and they want to sell); google uses it to guess what you will type next and search for; advertising uses it to find ways to connect individual products to users. Self-driving cars appear imminent. In education, Artificial Intelligence is becoming increasingly utilized for implementing today’s leading pedagogical trends, such as personalized learning. Analytics technologies allow us to do descriptive and diagnostic work; artificial intelligence will allow us to do more predictive and prescriptive work.
Time-to-Adoption Horizon: Four to Five Years
Mixed Reality is an emerging environment where digital and physical objects co-exist. The augmented reality game Pokémon Go is an example of this intersection. In education, virtual reality simulations have be used to train and asses medical students; first responders have trained in mixed reality environment overlaying hot-spots and other hazards. In the social sciences mixed reality tools have allowed for the virtual recreation of historical landmarks and allowed students to interact with virtual residents.
Robotics: The Harvard Business Review notes… “We expect the global industrial robot population to double to about four million by 2020, changing the competitive landscape in dozens of fields — from underground mining to consumer goods and aerospace manufacturing.” They go on to provide an example: “Foxconn, which employs more than a million workers in mainland China, plans to automate 70% of its assembly work within the next three years.” Higher education faces a significant challenge: preparing students for success in the next generation workforce and addressing corresponding emergent societal challenges.
I hope this exploration of the 2018 Higher Education Horizon Report has provided a window into the future. The report is provides a lot of ideas to fuel our themes of Technology, Education and Design. Next week offers a change of pace as I will provide updates from the 2018 Quality Matters Connect conference from St. Louis!
– Ted Witt
Teaching, Learning, and Technology Consultant
RESOURCES:
2018 NMC Horizon Report
Citation: Samantha Adams Becker, Malcolm Brown, Eden Dahlstrom, Annie Davis, Kristi DePaul, Veronica Diaz, and Jeffrey Pomerantz. NMC Horizon Report: 2018 Higher Education Edition. Louisville, CO: EDUCAUSE, 2018.
https://library.educause.edu/resources/2018/8/2018-nmc-horizon-report
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Examples and further Reading:
Learning Analytics: https://tech.ed.gov/learning-analytics/
Makerspaces: http://isam2018.hemi-makers.org/
Adaptive Learning: http://edtechreview.in/trends-insights/trends/2923-the-role-of-adaptive-learning-in-education
Artificial Intelligence: 7 Roles for Artificial Intelligence in Education by Matthew Lynch
https://www.thetechedvocate.org/7-roles-for-artificial-intelligence-in-education/
Augmented Reality: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271706077_Augmented_Reality_application_in_Higher_Education
Robotics: Building Tomorrow’s Robots by Gregory Mone
https://www.technologyreview.com/s/609004/building-tomorrows-robots/
The Age of Smart, Safe, Cheap Robots Is Already Here
https://hbr.org/2015/06/the-age-of-smart-safe-cheap-robots-is-already-here