Backward Design (Scholar Post)
A topic that I found interesting during our semester together was that of backward design. Teaching has evolved dramatically over the past few decades. It is becoming less about just “teaching” a subject, and more about making sure that your students understand what they are being taught, and why it is important to them when they graduate. This is largely due to more state and national standardized testing that students are required to take. Because of this, teachers are finding it difficult to plan for their classes. They want to make sure that students are getting the most out of what they’re required to learn.
We were first introduced to the idea of backward design in class during module 6 (class 4/13). I have heard about this approach in other classes, but I was learning about what it entailed. Now planning is going beyond just knowing what you’re teaching or what the state standards are for your subject. Now you need to know the knowledge of your students (Graff 2011). This is where we start to look at a great concept called curricular knowledge.
Curricular knowledge has two main parts. The first being horizontal, and the second is vertical. Graff does a great job at explaining these two types of knowledge. Horizontal entails the materials that students are studying in other classes, at the same time as your own. Vertical knowledge is the familiarity of what the students have already learned in your subject area, or what they are going to learn down the road (Graff 2011). Why is this important? Because to teach your students effectively you HAVE to understand what they already know, and what they don’t know. So after you have an understanding of where your students are, you can start to lesson plan. Backwards designing is just what it means, backwards planning. Where should a teacher start when creating a lesson plan that is backward?
The end goal of a backward design curriculum and instruction is for students to have a deeper understanding of what they’re learning along with retention and generalization (Chidre 2009). To ensure that this happens the way we would like it to there are specific steps that should be followed They include Identifying learners, identifying curricular priorities, design assessment framework, and create learning activities (Childre 2009).
Identifying learners is important for many reasons, but for your students to gain the most out of your class you need to understand their learning pattern. Do any of your students require special needs? Are any of your student’s ESL or ELL learners? After you have identified the learners individually it is important to identify your classroom needs as well. Are you more of a discussion based class? Or do you really like to lecture, and have the students note take? After you have assessed the learners you can move on to priorities.
Identifying curricular priorities is the second step. Here is where you will look at your state, and local standards. What is the knowledge that the children are supposed to gain out of your class by the end of the lesson? Other things that you could look at include are what your students should already know by the time they reach your classroom?
The third step is designing assessment framework. How are you going to get your students to learn what you want them to know? Childre (2009), explains “The aim is to move beyond recall of memorized facts to deeper understanding” (pg 9). This step helps you figure out how you want to test your students to make sure that they are gaining the knowledge you want them too. Will you quiz them? Have tests, or writing projects? The things you can do are really, endless. Once you have figured out you can get to the fun part, planning!
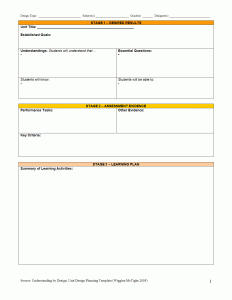
Step four is the part where you get to plan the activities for your students. This can be a fun, yet intimidating. Here I will bring in the template that we used in class.
As you can see, the template that we used in class really helps us get to the result we want for our students (class 4/13). The first thing that it asks the teacher to do is step one, which is the desired results. What are your goals? What do you want students to take away from your class? Then it goes into the understandings of the students. What do they already know? What do you want them to know? The second part of the lesson plan template allows you to plan for assessment. What will you have students do to show that they are learning the important information? What are other ways besides exams or projects that could show evidence? What criteria will the students be judged on? Lastly, you can use the large space to plan activities. These could include field trips, guided notes, and other fun activities to make the topic at hand interesting to learn. Along with this template, Wiggins (2012) does an awesome job at explaining why backward design is important in classrooms by having teachers continue to go back to their essential question, and make sure that they’re staying on track. He also has some great videos about creating a fantastic design for your classroom. Remember, Wiggins and McTighe (2005) explain that students are innocent of learning until they are proven “guilty” by the evidence the teacher uses.
In the end, I feel that backward design is one of the most effective ways to lesson plan. I really like starting with your goals, and explaining how you’ll get to them. Attached I have a video that does a really great job of showing why backward design can be important for every student!
References:
Childre, A., Sands, J. R., & Pope, S. T. (2009). Backward Design. Teaching Exceptional Children, 41(5), 6-14.
Graff, N. (2011). “An Effective and Agonizing Way to Learn”: Backwards Design and New Teachers’ Preparation for Planning Curriculum. Teacher Education Quarterly, 38(3), 151-168.
Wiggins, G., & McTighe, Jay. (2005). Understanding by design / Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe. (Expanded 2nd ed.).
Wiggins Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WsDgfC3SjhM
Filed under Uncategorized | Comments (6)
Final Thoughts
It has been a great semester! I will be walking away with some great information, that I will be glad to carry into my future classroom.
When it comes to being a great educator there are a few things that I think are extremely important. First, creating relationships. You are the one driving force in that students life for 9 months out of the year, 8 hours a day, 5 days/week. You must understand that student in order to effectively teach them. The second thing would be communication. Communicate, communicate, communicate!!!! Communicate with not only the student, but the parents, principal, other teachers, and other people who interact with that child on a day to day basis such as before and after school staff (me). That way we can all work as a team to help that student succeed. One last thing that is important as an educator is student centered learning. No child wants to sit all day and listen to lecture. Take their opinions into consideration, and tweak your lesson plans to incorporate their ideas. Has my opinion changed since the beginning of the semester? No, not necessarily. It never changes, It just evolves and grows. Working with students daily also helps with this. I take what I learn in the classroom and apply it to my after school program, and I can’t wait to implement it into my classroom.
Looking back this course has helped me prepare for almost every single standard. However, the two that stick out to me would be standard 3 and standard 7.
Standard 3: Teachers understand that children learn differently…..
This was shown to us in module four dealing with learner diversity. No one student is the same, we all come from different backgrounds. As teachers we need to learn to adapt our classrooms to everyone. I feel that this can also go hand-in-hand with standard 7.
Standard 7: Teachers are able to plan different kinds of lessons…..
Since all students are different, and all students learn different we need to be able to make all of our students successful members of our classrooms. Some students are visual learners, while others are hands on learners that is why creating a variety of ways to learn a unit is important. Motivation and instruction in module five did a great job of teaching us ways to implement that into our classrooms someday.
Backward’s designing will be taken with me throughout my career. I love being able to start with the final objectives of what I want my students to know, and then deciding how I am going to get them to the end goal. I will continue to research this throughout my college career.
I believe that our blogs were one of the best assignments that we could do. It is important to get ourselves out there for other professionals to see. This can help us gain new ideas from people who have different experiences then us. I will continue to use this blog until I graduate, and even after to always stay up to date on new and improved classroom tips. Good luck, everyone!
Enjoy this cute clip I found about teachers who made a difference!
Filed under Uncategorized | Comments (5)
Student Differences
All students are different. Each and every student learns in a different way. This can cause both excitement and frustration in the classroom. So, as a future teacher how do I expect to encounter differences among the students I will be working with?
Although I have not yet obtained my teaching degree, I have been working with children for the past three years at the Waukesha YMCA, and now the City of Waukesha Park and Rec department’s before and after school program. I have already encountered many different types of students. I have had students who are living in low income housing, with one or both parents working during all hours of the day. I have had students who are very fortunate in what they have, and also students who have a plethora of different disabilities trying to maintain a normal life at school.
I see it on a daily basis, so how will I plan for individual and cultural differences between students?
As mentioned above, I have already faced many challenges with the students that I work with daily. Differences in Socioeconomic status is one thing that I will run into. Woolfolk (2014), describes socioeconomic status as: “Relative standing in the society based on income, power, background, and prestige”. This is shown in the classroom in many ways. For example, Student A wears very clean, “new looking” clothes, always well rested, and fed while student B wears older clothes that are not as clean, and comes to school looking tired, and malnourished. Obviously, there are differences between them, and it most likely has to do with their socioeconomic status. It was said that the students who live in a lower income household will act more reserved, and quiet. This could be due to less encouragement, and support at home. This type of issue could cause resilient students. I feel that getting to know each student on a personal level as best as you can. Also using scaffolding will help all students learn. It is important to plan for differences so that we can see all of our students succeed.
I cannot wait to become an educator and create amazing students. I found a great video on YouTube about all different learners. Enjoy!!
Filed under Uncategorized | Comments (4)The Learning Theories
In class this past week we learned a lot about two of the different types of learning theories. The first being the biological approach, and the second one the cognitive approach. Digging deeper into them helped me gain an understanding of how I can implement both or just one of the approaches into my future classroom.
What are the main differences between these two approaches?.. According to Woolfolk (2014), “The cognitive view, knowledge and strategies are learned, then changes in knowledge and strategies make behavior possible. According to the behavioral view, the new behaviors themselves are learned” (p. 312). One of the main differences that I noticed during our lectures was that there was more reinforcement when it came to the behavioral approach. They do both use reinforcement, but behavioral approach uses it more. As teachers, why is it important that we apply these perspectives of learning into our instruction? There are many reasons why it is important, however as teachers we are constantly teaching our students new information. For instance, younger children need to learn proper manners. It was shown to us that the BOBO doll experiment that Albert Bandura conducted, that children who were showing aggression toward the doll were the ones who watched the adult before them be aggressive as well. This is a learned behavior. The cognitive approach will work well with older students who need to know a lot of new information, but that is being built upon older information already stored. Although these approaches to learning are important, they both have their limitations. It is explained in Woolfolk (2014) that rewarding students with learning could actually make them uninterested , and it could even cause them to have behavior issues in the classroom. The limitations with the cognitive approach could just be the fact that you are learning so much that it is overloaded into your brain and you don’t actually remember as much. As a future high school educator I believe that my classroom will benefit most from the cognitive approach to learning. I want them to be able to gain a deeper understanding of what they are learning, and be able to take the learning strategies I teach them through college, and the rest of their lives. When it comes to where I fall as an educator within the views of learning, again I would have to chose the social cognitive theory. I want my students to be able to take what they have learned in my classroom, and apply it to the real world. Ways that I can do this include a few of the following ideas. If I were teaching elementary students I would use a program called “My Classroom Economy”. This program is designed to help students learn responsibility, and money techniques. Each week a student is assigned a job, and they must do the job until the end of the week when they get paid. At the end of a month you can create a store where the students can spend the money that they earned. In a high school setting I would really like to incorporate Saundra McQuire’s successful learning strategies. I would be able to do this by making guided notes for my students, or just having them take in depth notes on their own, using the SQ5R meathod.
It is really interesting to learn more about how I can implement the different learning strategies into my future classroom, and I can’t wait to put them to practice one day.
If you’re at all interested in learning more about the My Classroom Economy program you can click on the link below :
https://www.myclassroomeconomy.org/
Filed under Uncategorized | Comments (7)
Student Learners
Here we meet again, this time only to discuss one of the most important parts of a classroom, the students. Our student’s are the sole reasons we become teachers. Am I right? We want to help the younger generation achieve greatness. However, in order to do that we must first understand how student’s learn. Let’s dig a little deeper.
How do student’s develop and construct knowledge? How do the developmental characteristics by famous psychologists impact teaching and learning?… I believe that students learn by doing. I think that is the way that they are able to get real life experiences both in and outside of the classroom. There are four main psychologists who each have great models and theories.
What are the main benefits and limitations of the models and theories?.. First, lets start by explaining who they are. We have Piaget who created the stages of cognitive development which has four stages. In grade school, where I’ll be working we have the concrete operational stage. This is where children “Can think logically about concrete (hands-on) problems” (51). Some of the benefits to Piaget’s model include the fact that it is very consistent and coherent. However, some people believe that Piaget may have overlooked effects of culture, and even social group. The next person on the list is Vygotsky. He uses the scaffolding method, and takes students just outside of their comfort zone to reach new learning potential. Some benefits to his model are that he is more sensitive to diversity, but he can be very vague, and he has insufficient attention to development issues. After Vygotsky, we look at Erikson. Erikson created the stages of psychosocial development. there were many benefits to this model including a child creating identity diffusion. However, what if a child gets “stuck” at a certain stage? Then wouldn’t they fall behind from their peers in school? I feel that could be a great disadvantage to them learning. Lastly, we have Bronfenbrenner who created the bioecological model of human development, and he also discussed the different types of parenting such as authoritative, and permissive. He had some positives to his model. For example, he explains that everything you do affects how you learn. If a teacher has a good learning environment, then it could positively affect their learning. However, on the contrary, if a teacher has a different style then the parenting then that could result in the student having a hard time with learning.
How can I take all of these theorists, and apply them to inform my future teaching?.. It is obvious that these models all work together inside of a classroom, and it is extremely important to incorporate all of them to help my student’s achieve higher learning. I am not a teacher yet, however I do work with an after school program. My school is an elementary school. I work with the age that Piaget would consider to be concrete operational. We do daily activities such as the question of the day. This requires my students to “dig deeper” and think of an answer. Vygotsky can be used in the future by having my students run a school store teaching them inferiority vs. industry. I will use scaffolding to help my students achieve what they almost know by challenging them. Lastly, I will take the time to understand my student’s not only as learners, but on a personal level. Getting to know my after school student’s on a personal level really helps me understand where they come from, and that can help me teach them.
I found this awesome video about a teacher who creates a handshake with all of his students. It is a great example of creating a one-on-one relationship with students
Filed under Uncategorized | Comments (2)
Teaching and Research
So, What is the relationship between research and teaching?… Teachers need to do research, or have someone help them do research so that they can continuously strive to become better in their field. Us teachers are teaching the next generation, and we need to find ways to help all of out students succeed. Research can help us make accommodations to our classrooms, and teaching methods for all types of learners.
So, How can I use information literacy to evaluate and select information about students and teaching?.. Well first of all I have to know what I’m researching. Let’s say I’m looking for research on Aspurger’s Syndome and learning math. First I have to know the issue, and the important parts of my research. Once I find the research that is most important, and helpful in my situation I can apply it, and help the child who has Aspurger’s Syndrome learn to the best of their ability.
What does this mean for my future career?.. I will be a constant researcher and learner in my career. I will constantly be researching new ways to help my students, and then learning how to apply it in the classroom to help all of my students achieve greatness.
Showing that I know how to apply research doesn’t have to wait until I am a teacher. In class we have talked a lot about the home work debate. Should homework be given to students? I started out believing that we should give our student’s homework. I mean, I was given homework all throughout grade school, and my academic achievements were just fine. However, while doing some research I started to feel the opposite way. According to Ronning (2010), some students who received homework actually did worse in their academics. Some even by 12 percent. This made me sit back, and think about what I was reading. Students who get homework actually can have a decrease in grades? This made me want to do more research on not giving out homework. This is where I found the article that Zimmerman and Kitsantas wrote. Research by Zimmerman and Kitsantas (2005) shows high school students, and the relationship between self-efficiency, homework, and GPA. It shows that there is a positive correlation with self-efficiency, homework, and GPA when the student is responsible. However, in elementary school it is half of the student’s responsibility, and half of the parents responsibility depending on how young they are. Again, this helps show that elementary students shouldn’t get homework. Even Marzano and Pickering (2007) state, “Although teachers across the K-12 spectrum commonly assign homework, research has produced no clear-cut consensus on the benefits of homework at the early elementary grade levels” (p.5). If it isn’t benefiting my students in the long run, why would I make them do it? They could be instead spending time with their families, and learning new skills at home and, according to Suhay (2015), “The schools that have given up assigning homework report uniformly fabulous results” (p.1). Although I started this research question with the opposite opinion that I now hold, I believe that it will benefit my future elementary school students the most if they are given no homework, and instead encouraged to spend time with their families, and learn new skills at home.
Marzano, R., & Pickering, D. (2007, March). Special Topic/ The Case For And Against Homework. Educational Leadership, 64(6), 74-79. http://www.lincnet.org/cms/lib05/MA01001239/Centricity/Domain/108/Homework.pdf
Ronning, M. (2011). Who benefits from homework assignments?. Economics of Education Review, 30(1), 55-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.econedurev.2010.07.001
Suhay, L. (2015, March 6). New York school abolishes homework. Does homework do any good?. Christian Science Publishing Society. Retrieved from https://libproxy.uww.edu:9443/login?url=http://search.proquest.com/docview/1660974352?accountid=14791
Zimmerman, B.J., & Kitsantas, A. (2005). Homework practices and academic achievement: The mediating role of self-efficiency and perceived responsibility beliefs. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 30(4), 397-417. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2005.05.003
Filed under Uncategorized | Comments (7)My Story
When most kids are asked what they want to be when they grow up, their answer may change several times throughout their childhood, and teen years. Mine? It always stayed the same. I ALWAYS wanted to be a teacher. I was considered the “teachers pet” in my class every year, I was the student that my teachers would bribe to go outside for recess because I never wanted to go. I always had cool ideas, and although my teachers complained that I had too much to say, the “children” that I taught in my “classroom” at home (which consisted of a desk, a dry erase board, and one science textbook) never said a peep. I would spend a lot of my free time as a child “lesson planning” for my students, and once I reached high school I knew that teaching was the route I wanted to go. In the Summer of 2015, after my sophomore year of college at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee I accepted a job at the Waukesha YMCA as a summer camp counselor. I was extremely nervous as it would be the first time I was really interacting with children on a day to day basis. Taking that job ended up being one of the best decisions I’ve ever made, and that is what ultimately influenced my decision to become a teacher. I created some amazing friendships not only with the staff, but being with the same 30 kids, ten hours a day, for eleven weeks creates incredible bonds that I will never forget.
After my summer as a camp counselor I was offered to be a part of the before and after school staff at Whittier Elementary School in Waukesha, Wisconsin. I quickly snatched the position and began working with kids in the after school portion of the program. I was lucky enough to have a sneak peak of what being a teacher would be like. I was able to help students with their homework, and also give ideas as to what activities I thought the children would like to do.  Whittier is a very low income school, and unfortunately they have a lot of problems behaviorally. However, there is nothing more satisfying then watching a child understand something that they didn’t before especially when you taught it to them. Making a difference in a child’s life is a great feeling. A lot of the children that I worked with at Whittier didn’t have great role models in their life, so for me to be an influence in theirs was an amazing feeling. I have many great stories that I will forever cherish, and I will carry with me forever. I am now a site coordinator at Meadowbrook Elementary School in Waukesha, WI, and although it is a different dynamic then that of Whittier I still make just as much of a difference in the lives of the children around me. Working in schools for the past year, and being in school for quite a while have helped me understand what does and what does not make a good educator. Like we discussed in class, the best educators are the ones who have a sense of humor, know their content, and are passionate about their students learning. I think that humor is a must when working with kids, and I have implemented that in my current position, and plan to carry that with me in my own classroom. The late Robin Williams shows great enthusiasm in his classroom during the short video we watched. It was amazing to see his students go from bored, and uninterested to completely consumed in what he was teaching.
Whittier is a very low income school, and unfortunately they have a lot of problems behaviorally. However, there is nothing more satisfying then watching a child understand something that they didn’t before especially when you taught it to them. Making a difference in a child’s life is a great feeling. A lot of the children that I worked with at Whittier didn’t have great role models in their life, so for me to be an influence in theirs was an amazing feeling. I have many great stories that I will forever cherish, and I will carry with me forever. I am now a site coordinator at Meadowbrook Elementary School in Waukesha, WI, and although it is a different dynamic then that of Whittier I still make just as much of a difference in the lives of the children around me. Working in schools for the past year, and being in school for quite a while have helped me understand what does and what does not make a good educator. Like we discussed in class, the best educators are the ones who have a sense of humor, know their content, and are passionate about their students learning. I think that humor is a must when working with kids, and I have implemented that in my current position, and plan to carry that with me in my own classroom. The late Robin Williams shows great enthusiasm in his classroom during the short video we watched. It was amazing to see his students go from bored, and uninterested to completely consumed in what he was teaching.
I could sit here and tell all of you what I think makes a great teacher. We could go back and forth all day discussing what we think makes a good teacher. However, there is one opinion that should matter most when it comes to us becoming a great teacher. It comes from the student. I found this great video that I would love to share about what students in Madison Public Schools think make a great educator. I hope you all enjoy!
Arsenault L. (2013 August, 26).”What Makes a Good Teacher?” [Youtube]. Project: Blog.
Filed under Uncategorized | Comments (4)Hello world!
Welcome to Blogs.uww.edu. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start blogging!
Filed under Uncategorized | Comments (8)