Communication Styles

An important aspect to learn about before visiting Rome, Italy is their culture’s communication style as well as how they manage conflict. Rome, Italy’s communication style regarding how they converse with others can be crucial to know so that we can exchange meaningful cross-cultural interactions and become more interculturally competent.
High-context vs. Low-context
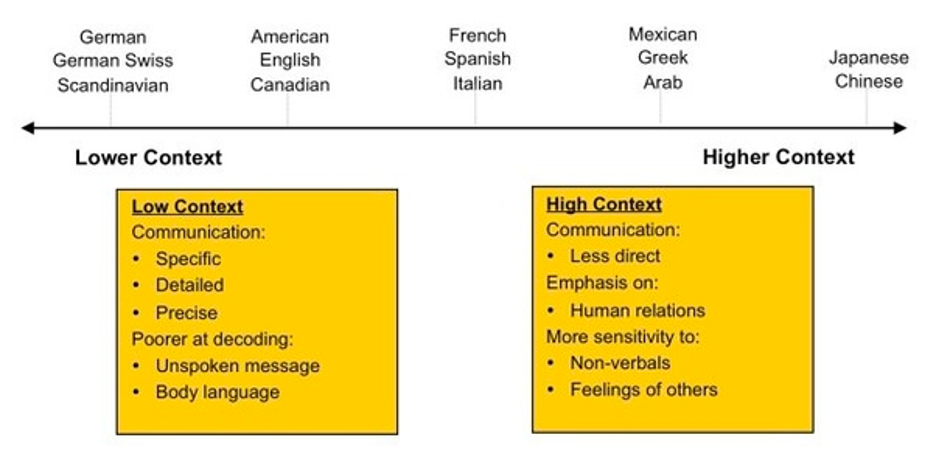
A way to understand Rome, Italy’s communication style is through the terms high-context and low-context. High-context cultures are less direct with words, placing emphasis on physical cues, while being more sensitive to non-verbals and the feelings of others. They focus on the underlying meaning and tone of the message, not just the words themselves. Whereas, low-context cultures are specific, detail oriented, and rely heavily on the words themselves (Miller, K. 2022). Rome, Italy is considered a high-context culture, meaning they place emphasis on physical cues, rather than analyzing the message (Fleming, E. 2020, January 8). This means that if you are communicating with someone in Rome, they might use physical cues such as speaking with their hands in order to communicate effectively. Knowing that they are more sensitive to non-verbals and the tone of the message, not just the words themselves is important to understand when it comes to exchanging interactions. This is an imperative aspect to keep in mind before visiting Rome, Italy because if you are an American, it can be hard to decode body language and physical cues, as American’s place emphasis on precise detail while communicating with others. Having awareness that Rome, Italy is a high-context culture can help you comprehend how that culture communicates, so if you ever visit you can exchange meaningful cross-cultural interactions.
How Communication Styles Affect Conflict
Differences in communication styles between cultures can lead to misunderstandings, potentially conflict, altering how conflict is perceived or responded to. Elizabeth Bowen, author of the reading, Cultural Diversity in Perception: Alternative Views of Reality, states “As Ting-Toomey has observed, the communication differences between high-context and low-context cultures are also apparent in the manner in which each approaches conflict” (Bowen, 81). In other words, it is important to understand Rome’s communication style, as it manifests how conflict is approached in a communication situation. For example, high-context cultures such as Rome, Italy approach conflict with the view that it is damaging to interactions. In result, high-context cultures use indirect communication often avoiding or withdrawing from the issue using silence to resolve the conflict. On the contrary, low-context cultures such as America approach conflict with confrontation, often implying direct communication and collaboration between both parties to find a solution (Miller, K. 2022).
Knowing these differences can aid in preparation for visiting Rome, as you can become more aware that these differences in communication styles exist, which can manifest how members approach conflict. For example, if you are in a communication situation with someone in Rome, and there’s a misunderstanding that leads to an intercultural conflict, you may anticipate that they might simply walk away and avoid the underlying issue before you get a chance to confront the problem. I personally have had intercultural conflicts in Rome, Italy due to the differences between communication styles, and there was an instance where a member from their culture walked away from me during an interaction, because that is how they approach conflict. Me being an American, tried to approach the conflict with direct communication, however since both parties misinterpreted the communication styles, the other person simply decided to withdraw from the situation. Understanding not only how your own culture communicates, but how another culture such as Rome, Italy communicates is crucial to becoming more interculturally competent, as these aspects go hand in hand with being able to make meaningful connections and establish intercultural relationships.
By: Lindsey Buchanan
